Gingivitis Treatment
The Prevention and Treatment
of Gum Disease
age-well.org > look well > gingivitis treatment
What is Periodontal Disease?
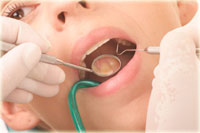
Gingivitis treatment is often necessary as we age and develop gum disease.
Periodontal disease is another name for gum disease. It is a health condition usually arising from poor oral hygiene when plaque is allowed to build up around the base of the teeth causing inflammation.
Gum disease starts when a sticky white substance, known as plaque is formed when saliva mixes with mucus and food residue from starch and sugar in the diet and coats teeth. It starts to build up in the spaces between teeth and gums that becomes infected by bacteria and causes inflammation and swelling below the gum line. It eventually starts destroying gum tissue, and in advanced cases even starts destroying the ligaments and the tooth sockets.
What Is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis or inflammation of the ginviva or gums is a type of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is due to the long-term effects of plaque deposits.
When plaque is allowed to remain at the base of the teeth it hardens into an irritating deposit known as tartar that is trapped in the base of the teeth and irritates and inflames the gums making them swell up and become tender. Bleeding often occurs, even when the teeth are brushed very gently, which is the main indication that gingivitis treatment is necessary. Gums may begin to recede.
Once tartar has built up it is hard to remove with normal cleaning and you will probably need a professional cleaning. After scraping the plaque from around the base of your teeth, the dental nurse or dentist will show you how to keep the tartar from building up again by proper cleaning. Professional cleaning can reverse gingivitis.
Brushing or flossing the teeth too vigorously can also lead to gingivitis as can injury to the gums from any other cause, including overly zealous cleaning from the dentist. If this happens gingivitis treatment may also be necessary.
People with diabetes are particularly vulnerable to the disease and should pay special attention to dental hygiene. Poor general health and dental hygiene in general can also make us vulnerable to this condition as can the hormonal problems caused by pregnancy and the menopause. Other contributory factors are misaligned or crooked teeth, and ill-fitting and un-clean braces, dentures, bridges and crowns, as well as the rough edges of old or broken fillings.
Certain medications and metals such as lead are also associated with the disease.
Trench Mouth or Vincent’s Stomatitis
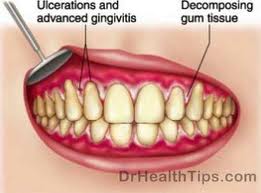
Another medical condition which effects the gums is known as trench mouth because a lot of soldiers developed this disease during the first world war, when it was difficult to practice good dental hygiene in the trenches and the fighters were often suffering from poor health and lack of vitamins, especially vitamin C.
These soldiers were obviously also subject to a lot of stress and stress is known to be another contributing factor to trench mouth and other gum diseases.
Trench mouth causes bad breath, ulcers, fever a bad taste in the mouth, swollen red gums, which are often covered in a grey film and are irritation, painful and bleed when touched. It can lead to tooth loss and the destruction of gum tissue and tooth loss.
The more scientific names for this disease are Vincent's stomatitis or acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
You should consult a doctor if you think you may have this disease that usually affects young adults between the ages of 15 and 35. In the meantime treat it with brushing and washes in salt water several times a day.
Good nutrition and better general health, regular professional cleaning, good dental hygiene, learning to cope with stress and stopping smoking can all help prevent this disease from reoccurring.
What is Periodontitis?
If you suffer from gum disease and the bleeding is combined with pain, this is a signal that the inflammation and infection has now invaded the deeper gum tissues and the bone, which is a more advanced condition known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis is responsible for more tooth loss than cavities in patients over the age of thirty
How do I know if I have gum disease?
The main symptom of gingivitis or other periodontal disease is bleeding gums. Other telltale signs are shiny, soft, swollen purple or deep red gums that are tender to the touch and bleed when brushed even gently and the build up of tartar at the base of the teeth.
Often the disease may be pointed out to you when you visit the dentist. He will usually suggest a professional cleaning and show you how to brush and floss correctly and direct you to do so morning and night and after every meal, at least as far as brushing the teeth.
Keeping Gums and Teeth Healthy
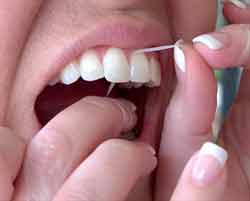
Teeth should be brushed at least twice a day, morning and evening, preferably last thing at night before sleeping. People with chronic gum problems should also clean the teeth after every meal and snack.
Using a mouthwash made up of warm water with salt or tea tree oil after brushing will also help keep the mouth clean and healthy.
Flossing should generally take place once a day preferably before bedtime. Make sure you don't damage the gum by too brisk movements. The gums can also be massaged daily with utensils specially shaped for this purpose usually from wood or plastic, which helps to strengthen the gums.
Extracting teeth in the case of overcrowding and realigning the teeth is recommended during adolescence to prevent the build-up of plaque between the teeth and make cleaning easier. Often this is not possible for financial reasons and it is not as successful in later life.
If teeth are very over-crowded the dentist will often recommend a professional cleaning twice yearly. The new electric brushes with oscillating head, such as Oral B, can be useful for people with crowded teeth or a tendency to develop plaque.
Bleeding and tenderness of the gums should lessen within a few weeks after professional cleaning and careful oral hygiene should be maintained thereafter. If this is not done the condition will surely reoccur.
Natural Means of Gingivitis Treatment
Warm salt water or antibacterial rinses can reduce swelling and protect the mouth from bacteria. As commercial mouthwashes have been blamed for a variety of conditions, I suggest rinsing your mouth with a solution containing tea-tree oil and hot water.
Both Tea tree oil and salt can be used as mouth washes for gingivitis treament without a fear of side effects. Tea tree oil toothpaste and massaging the gums with tea-tree oil gel can also help people who have chronic gingivitis.
Vitamin C is believed to help gum disease because this vitamin has antioxidant properties that are needed to repair connective tissue and accelerate bone regeneration. See our article on Vitamin C to learn how to get your recommended daily dose.
Vitamin D may reduce susceptibility to gum disease because of its anti-inflammatory properties. Sun exposure is one of the most important sources of vitamin D, because UV rays from the sun trigger the synthesis of vitamin D in skin. Health professionals suggest exposing the skin to between 10 to 15 minutes of sunshine at least twice a week in order to help you get enough Vitamin D.
Stress contributes to the build up of the plaque that can trigger gum disease and you should consider ways to relieve stress including relaxation techniques, meditation and correct breathing exercises.
Cranberries are believed to help bacteria from building up at the base of the teeth. If you drink the juice make sure it has no added sugar. Learn more about Cranberries here.
Back to the Basics
To recap on gingivitis treatment and how to prevent gum disease and keep your mouth healthy:-
- Good oral hygiene is the best prevention against gum problems because it removes the offending plaque.
- However, you also need to improve your general health by good nutrition, exercise and developing good habits
- In particular, quit smoking.
- Remember that teeth should be brushed at least twice a day – in the morning and at night.
- For people who have a tendency to develop gum disease, looking for a more effective gingivitis treatment or wish to prevent reinfection, it is also recommended to brush after all meals.
- Floss once a day taking care not to injure the gums.
- Use a toothbrush with oscillating rotating electric head.
- Use specially designed wooden or plastic utensils to massage the gums to strengthen them.
- Use water picks if you have crowded teeth.
- In all cases, if you can afford it, have your teeth professionally cleaned at least every 6 months.
Resources
Page on Oral Hygiene
Page on How to Eat Well
Develop Smart Habits
Quit Smoking
(Source: American Academy of Periodontology. Parameter on plaque-induced gingivitis. J Periodontol. 2000;71:851-852. pennstatehershey.adam.com and About.com website pages on care for the gums and gum diseases)
age-well.org > look well > gingivitis treatment
Top of Gingivitis Treatment
Back to age-well.org
Enjoy this page? Please pay it forward. Here's how...
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment,
your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.